-> 29 May
Sequencing frame
If we wanna input a sequence into our paper, we need to think about:
- How many frames
- How long
- What key moment
- Is it a logical change
- Storyboard – Camera change?
Does the shot work to convert your message?
Depending on what you want to say, choose a close-up or other focus lens. Think about the cus and dissolve transit.
The other thing about framing is constructing our information as well. Think about how to reveal a character. Is it revealing a shoulder first? Why did we choose this particular shot? Why do we use this angle?
Invisible techniques: ( Peter Ward, Picture Composition for film and television ) ( 1996 )
Some skills are like golden portion or sweet point. The animation should work without voice-over or audio, which is just for enhancing the visual.
For example, in Shrek, you will notice the camera moving slowly. In post-production, it is sometimes hard to achieve this slow movement naturally. And, for the next scene, the camera should still move to keep consistency when the two people are talking when we swift the camera.
Ward suggests a framework to evaluate whether the sot or composite achieves the makers’ intentions or objectives.
- Is there something behind you? Is there a reason for that?
- what elements in the shot maintain visual interest.
- Does the image attract people’s attention
- If you want to use an abstract image, think about why it is there.
- Maybe, in 2D, it is easy to use morphing transit. Maybe, in 3D, it is crystal to use something to be a transit-like dissolve.
For a 25-second commercial, if you don’t use lip sync, your visuals need to be highly engaging. Consider techniques to capture the audience’s attention, such as a camera drop, similar to popular TikTok trends. Many CGI projects incorporate VFX to draw viewers in, avoiding the use of too many abstract objects.
–
Some terminology we learn today:
Staging and blocking
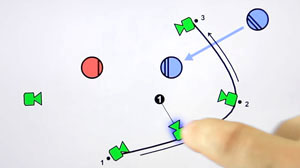
- Staging: choice of a shot. It can emphasize emotion.
- Nicholas Proferes ( 2004), Film directing and fundamentals, chapter 4: In film, the camera can be everywhere.
- Staging can indicate the nature of a relationship
- Staging can orient the viewers.
- Staging can resolve spatial separation. ‘Separation’ occurs when a character is shot within a frame.
- Staging can direct the viewers’ attention.
- Always ask yourself: why do you use this shot? Is it relevant?

-> 22 May
Review the research proposal structure
- Research title or question
- Draft Intro
- Keywords
- Drafts literature review -> Most of the content
- A draft chapter -> Most of the content
- General outline of each chapter
- Indicative bibliography
Tips for Critical Thinking
- No personal feeling
- examing data from different angles
- check the accuracy of the information
- check the logic of the argument
- Look for possible flaws in the statement
Key questions:
- WHY? WHO says?
- The main point behind the question?
- Is this true? why?
- reliable of the information
- challenges your own thinking
- Can I back up my point?
Thinking critically in assignment
The most common objection: reports are descriptive, not analytical.
Descriptive writing:
- Tells the reader what you have done
- Tends to use lots of quotes
- Gives a summary
Critical writing
- Difference: critical vs Descriptive
Critical thinking
- Like a criminal investigation
- Before the proposal, it is hard to have a conclusion since you have not done the research.
- Formal: third person. ( it was found that…. )
- Tentative: It has been suggested that it could…
- Always give a logical reason.
- The best way: You keep noting and feel confident. You know all the things you wrote.
Go back to talk about some terminology. Make sure you are using the right and specific words.
Develop your own academic voice:
- Scepticism. Not cynicism.
- Critical writing style tip: choose a format and stick to it.
- Draft > revise > edit
- Critical writing: Rhetoric -> a gentle art of persuasion
Ual referencing
Resources to learn how to write referencing.
List: ( Connect with learning resources )
How to do Harvard Style Referencing
A Quick Tour of Cite Them Right

-> 15 May
Research design
20 types of research design
Case study part, we should include:
- Title
- Overview
- Problem
- Solution
1. Exploratory research design
Experimental research
- Hypothesis
Field research
Suggest you go to a festival.
Survey
You have to prepare so many things well.
Meta-analysis research design
Mixed-method research design
You may do both or not only two methods.
Longitudinal research design
You need to do more than two years of survey.
Just learn that we come across that we have different types of research methods to use in our paper.
Research objectives
Think well these points:
- Your title of topic
- Identify the main title, subtitle
- Make sure that’s the question you can answer
- Pinpoint the major of your research
- You might be able to prove that
- Break down your main focus into subjective ( think it is not too objective )
- Smart system! Measurable and achievable. ( there is a website where we can get an idea of how it works )
- Be specific about your outcomes.
- Make your object relevant to your research
- Time-based: show your process on track.
Tips:
- Be concise. Try to avoid unnecessary. For example, Pixar is an important company. You can just go straight of it. Avoid the fact people know. Avoid anything like this.
- Keep your number of objectives limited. ( that’s too many ) Think of narrowing it down.
- Use action words. Show confidence in your attitude.
- Be realistic! Make sure you can conclude the things. Sub-conclusion. ( How does that answer your overall question. )
The craft of writing
- Each week, make sure you move on and work on the progress.
- Set yourself small challenges.
- Find a resource and start to keep notes.
- When it comes to reading, you start by reading something useful, googling it, recording it, or grabbing key points from your paper at the same time.
- Make judgments about the strengths and weaknesses of the study and write them down.
- Make notes when we are searching and collecting. The process will be to collect, make notes, and advise ideas.
- About making a note, you don’t just copy and paste. Wrote your own words!! ( Can be really simple ) -> establish critical thinking.
Critical evaluation
- Tell readers why you start this topic
- Internal validity ( not the things you are going to much ) if you are doing a survey or questionnaire.
- Try to find resources to help you better understand. ( A link to an article on how you would have internal validity.
The golden thread
A video introduces what it means.
Check the topic -> background and intro -> Lit review
- Help you organize your thesis. ( structure )
- Tie up all the content of all your content together.
- A way and method to your research questions.
- Make sure the section ( open up the footers and page number ) Good tips
- Use a checklist you can use! Choose the keywords of your questions or title. Pick the keywords and make sure you talk about all of them in your content.
Make a checklist of your thesis and make sure you cover all keywords you mention.
Example
- Background and introduction. ( where is the research ) Who is your target?
- Primary question? The secondary Question is?
- Lit Review: Your point 1 ( Reason one or statement ), Point 2, and Point 3. Each instance needs to be explained. (Use the Same tips in the checklist.) In the chapters, background and this technique can also help you check.
- Out of alignment.(A picture)
In alignment:
O-O-O-O-O-O ( like this )
Tile -> problem statement and research questions -> points in Lit review
research design and method
- show your keywords in each chapter like this ( A, B, C )
The overall structure will be like this – Key concepts ( ABCDEFG )
And then, circle some keywords you will cover or measure that fit your topic. ( ABCD ) Also, make sure you cover the main keywords you mention in the main questions.
Tips
- create a visual board!!
- Keywords checklist and make sure you are in alignment and consistency of what you said is related to your overall questions.
Chapter title -> It needs to be aligned.
- When you start to write, you will know and recognize the structure thing.
- Recognize your keywords all the time.
- Refer back to your questions.
You are exploring your research. The tips above are good tips for your structure.
1500 words
